In this article we explore the question, “What is physical literacy?” and how it relates to the world of physical education. In addition, we break down some of the key concepts of physical literacy and discuss PLT4M’s role in the pursuit of supporting students lifelong journey of health and wellness.
What is Physical Literacy?
Over ten years ago, researchers first set out to answer the question, “What is physical literacy?”
“Physical literacy is the ability to move with competence and confidence in a wide variety of physical activities in multiple environments that benefit the healthy development of the whole person.” (Mandigo, Francis, Lodewyk & Lopez, 2012)
And over the years, we have continued to seek answers and definitions to the question, “What is physical literacy?” And beyond just ability, people have started to look at the importance of motivation and attitudes toward physical fitness and activity. As a result, we have broadened our answer to better guide our promotion of physical literacy.
Check out the definition from The Canadian Assessment of Physical Literacy,
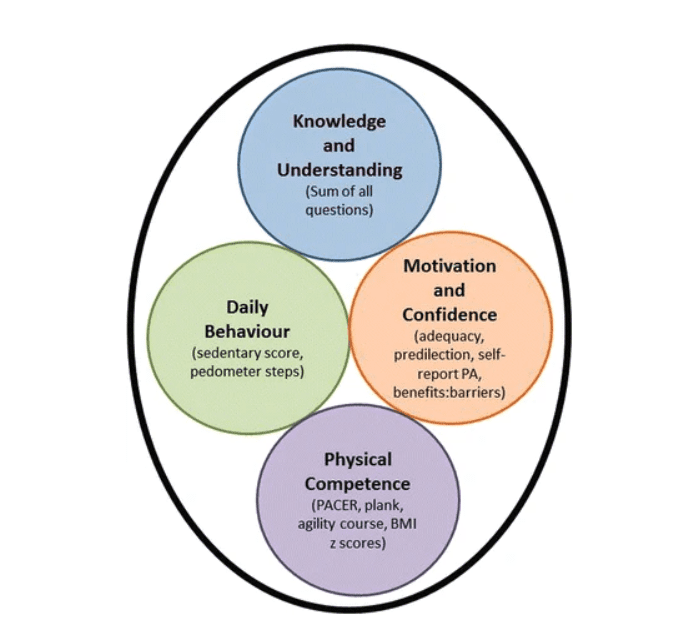
“The internationally accepted definition of physical literacy was published during CAPL development. It recognizes four essential elements of physical literacy: motivation and confidence (affective), physical competence (physical), knowledge and understanding (cognitive) and engagement in physical activity (behavior).” (Whitehead M. International Physical Literacy Association. https://www.physical-literacy.org.uk/ 2014.)
Physical Literacy & The Importance of Physical Education
An individual’s physical literacy journey can start at an early age. For example, physical literacy development occurs during activities like learning to ride a bike or participating in youth sports.
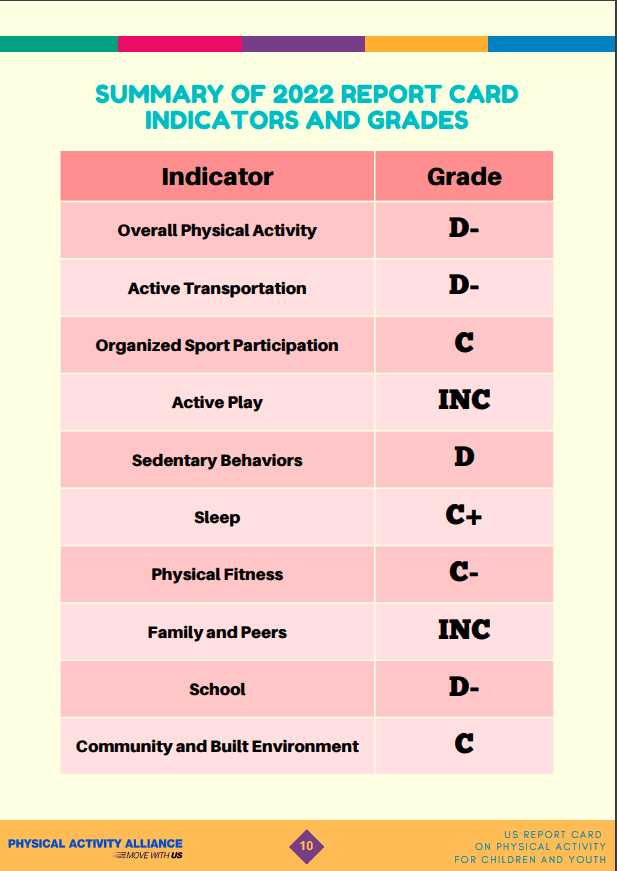
And while some have argued that physical literacy development can happen organically and without the help of schools, the physical activity participation rates would beg to differ. In fact, we have either a C or D grade in every category on the 2022 Report Card on Physical Activity for Children and Youth. That means not only are physical activity levels low, but children and youth aren’t participating in the places where physical literacy is developed.
But even if the US was topping the charts for physical activity levels (which we aren’t), we would still make a case for physical literacy development in physical education programs. And that is because physical activity engagement is only one component of physical literacy. (See more here on the differences between physical activity vs. physical education.)
Physical literacy is about learning a wide range of functional movement skills across different activities. A quality physical education program goes beyond skill building and teaches students about healthy lifestyles through fitness, nutrition, health, and more. A physical education program presents the best opportunity for every student to grasp physical literacy in all of its parts.
What is Physical Literacy in Physical Education?
Physical education programs have pushed to better understand the question, “What is Physical Literacy” in the context of different developmental stages.
Historically, entire K-12 physical education programs have centered around sport skills and games. And while understanding these concepts and skills is essential, it is only a piece of the physically literate individual.
As a result, many primary physical education programs have continued developing these skills with young children, while secondary education programs have shifted to a fitness-focused curriculum. In this curriculum model, students learn and develop functional movement skills like squat, lunge, hinge, press, and pull. And over time, students can take these functional movement skills and apply them to a diverse range of physical literacy domains like fitness, yoga, dance, pilates, boxing, bootcamp, strength training, and more.
Again drawing back to the definition, we want to equip students with skills that will support them throughout their physical literacy journey. Because as students grow into older adults, sports will not always be a fitness option. Instead, healthy active choices will revolve around working out at home, the fitness center or gym, and beyond.

What is Physical Literacy For PLT4M?
At PLT4M, we believe in the importance of physical education and help to answer the question, “What is physical literacy?” Using the pieces from the International Physical Literacy Association, let’s explore each piece and how PLT4M supports physical literacy.
Physical Competence – With PLT4M, students are introduced to fundamental movement skills to safely and effectively exercise during physical education and beyond. And we do this in a wide variety of physical literacy domains.
Knowledge and Understanding – Beyond just fundamental movement skills, PLT4M layers in video and written instruction to deepen learning for students in physical education. Yes, we want students to be physically active, but we also want them to know the what, why, and how behind healthy lifestyles.
Motivation and Confidence – For many students, confidence is key for physical activity participation. Within PLT4M PE lessons, we encourage scaling and modifying movements to find the right fit for each student. In addition, our technology motivates and inspires students with real-time feedback and progress reports.
Physical Activity Engagement – With the myriad of choices within PLT4M, we help students find the physical activity and fitness options that they enjoy. Once physical activity is a choice, students need options that they enjoy and will continue past the walls of physical education.

Ready to Learn More?
Schedule a free 10 minute consultation to see how PLT4M can help save you time and empower student learning!
Key Takeaways on Physical Literacy
The healthy development of children isn’t just about reading, writing, and math. And while literacy is often a term utilized in other areas of education, physical literacy helps to create common terminology for the world of physical education. As a result, we can better understand the importance of physical education for our children of all levels.
The key takeaways are clear:
There are multiple environments that children can develop physical literacy.
Physical inactivity is a growing problem in the united states.
Increased physical activity is part, but not the complete solution to physical literacy.
Physical educators play a crucial role our children’s physical and health literacy.
An increased investment in physical education can support long-term health outcomes for children now, but also as they become adults.
FAQ
What types of high school physical education activities do you cover?
Our ever-growing library of original content includes a variety of programs intended to spark lifelong physical literacy. Check out the options below:
Is PLT4M Standard Aligned?
Yes, Shape America is one of the biggest advocates for physical literacy. And PLT4M is a proud partner of Shape America and all PLT4M programs are aligned to the Shape Standards.
Is physical literacy the same as long-term athlete development?
Long-term athletic development (LTAD) is a popular model for teaching and training students and athletes. LTAD refers to a practical approach to fitness and athletic education. It takes physical activity and teaches it like we do any other subject: through progression and planning. And in many ways, it is very similar to the term and approach to physical literacy with some nuances and differences. But long story short, an LTAD model supports many of the same goals as physical literacy.